Hepatitis C virus (HCV) affects 2.4 million Americans and can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma if left untreated. Viral cure is achievable in most patients with treatment given the high efficacy of current eight to 12 week oral regimens combined with favorable safety profile. HCV cure following therapy is not confirmed until HCV RNA remains undetectable at 12 weeks after the end of treatment. This is known as sustained virologic response (SVR) and can be considered viral cure, as relapse after 12 weeks is exceedingly rare.
The AGA quality team has developed this quality measure to guide you in providing high-quality care of patients with chronic HCV.
Quality measures to track:
Sustained virological response (SVR) in the treatment of hepatitis C infection.
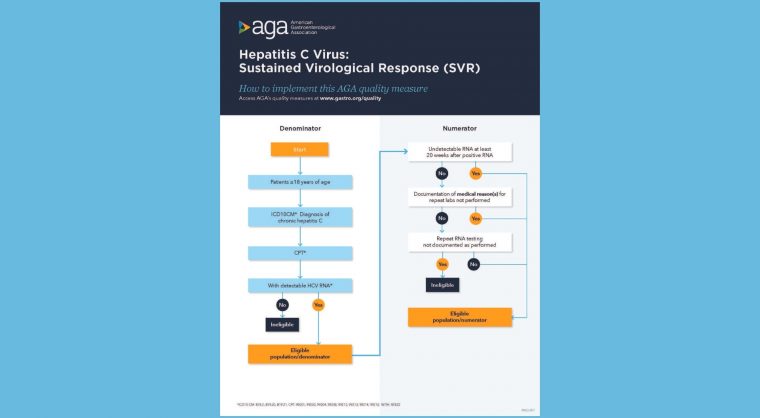
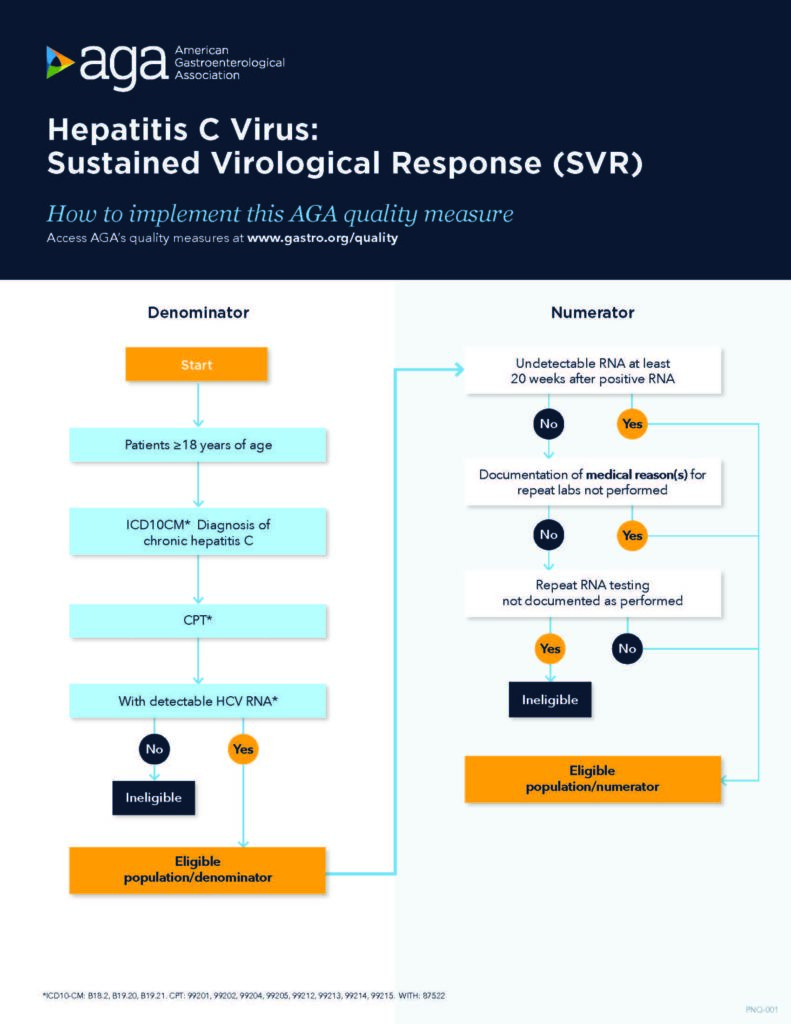
In patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic HCV and positive HCV RNA, treating providers should confirm and document SVR with an undetectable HCV RNA test at least 20 weeks after last lab with a positive RNA. (20 weeks is intended to capture the minimum duration of therapy with the necessary time to wait to test for SVR).
Quantifiable process and outcome metrics to track
Process metric: Percentage of patients with chronic HCV with undetectable HCV RNA at least 20 weeks after last lab with positive RNA excluding those situations where clinician documents rationale for not obtaining initial or repeat labs during HCV therapy.
Use our measure implementation flow charts:
Learn more about AGA’s quality measures and view our complete list of quality resources.